Defensive Strategies
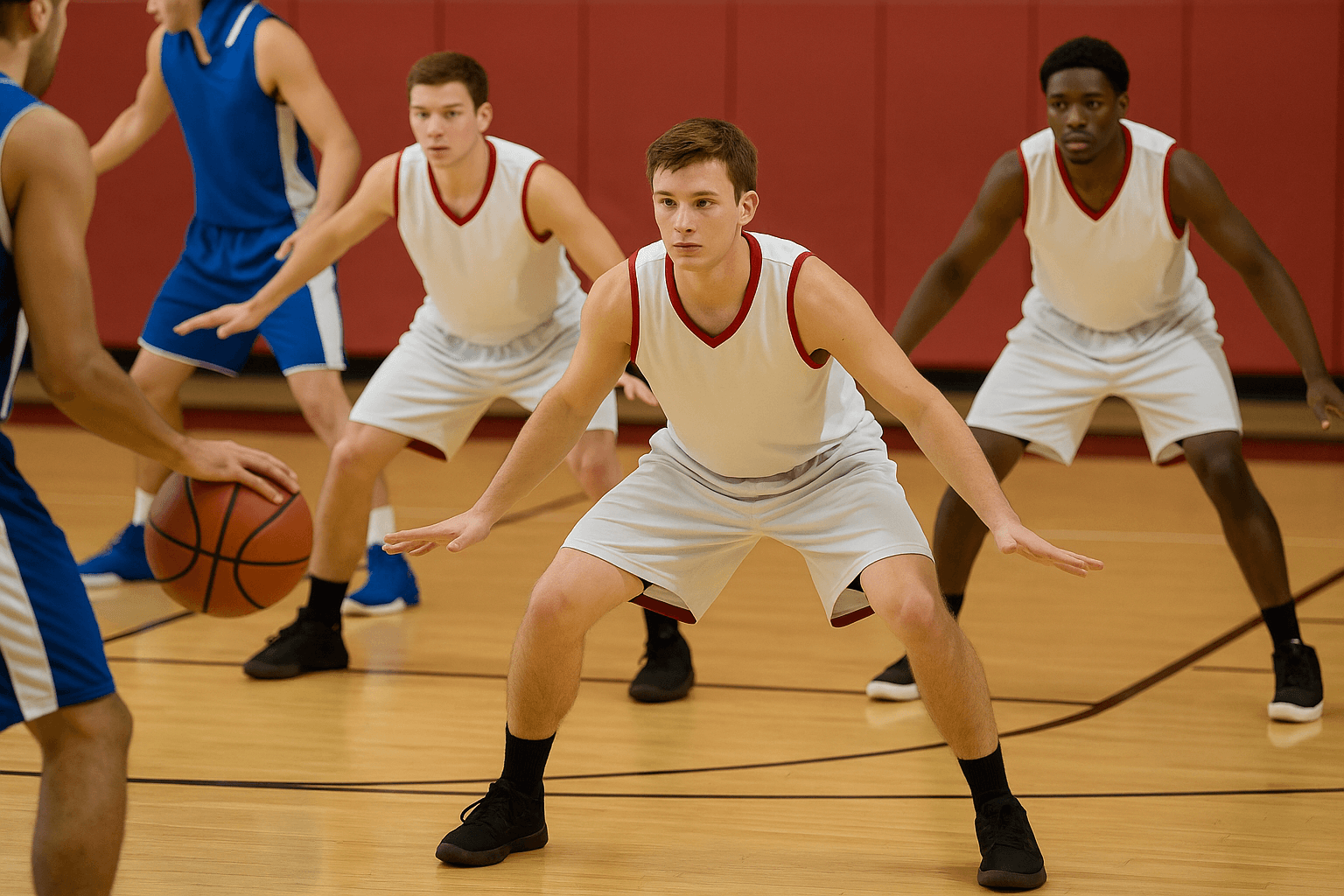
A basketball team sets up in a 2-3 zone defense, showing teamwork, communication, and discipline.
Defensive Strategies in Basketball: How to Stop Your Opponent
The saying goes, “Offense wins games, but defense wins championships.” In basketball, strong defense is what keeps opponents from scoring and creates opportunities for your team to take control of the game.
This guide explains the main defensive strategies, how they work, and why they are so important.
Why Defense Matters
Great defense makes life difficult for opponents. It forces bad shots, creates turnovers, and gives your team more chances to score. Without defense, even the best offense can’t win consistently.
Benefits of Strong Defense
- Prevents easy baskets
- Creates fast-break scoring chances
- Builds team confidence and toughness
- Wins close games
Problems Without Defense
- Allowing too many easy points
- Struggling to stop opponents’ best players
- Falling behind quickly in games
- Wearing down physically and mentally
Types of Defensive Strategies
Man-to-Man Defense
Each defender guards a specific opponent.
- How It Works: Players stay close to their man, deny passes, and help when needed.
- Benefits: Good for pressuring the ball and taking away individual strengths.
- Example: A guard stays locked on the opposing point guard, contesting every dribble and shot.
Zone Defense
Players guard an area instead of a single opponent.
- How It Works: Defenders cover zones (like 2-3 or 1-2-2) and move together to protect the basket.
- Benefits: Helps against teams with strong individual players or size mismatches.
- Example: In a 2-3 zone, three defenders protect the paint while two cover the perimeter.
Full-Court Press
A high-pressure defense that starts as soon as the other team inbounds the ball.
- How It Works: Defenders trap, pressure, and force mistakes before the opponent crosses half court.
- Benefits: Creates turnovers and speeds up the game.
- Example: A 1-2-1-1 press traps the ball handler in the corners, forcing risky passes.
Trap Defense
A trap involves two defenders pressuring the ball handler to force mistakes.
- How It Works: Defenders corner the ball handler and cut off passing lanes.
- Benefits: Forces turnovers and bad decisions.
- Example: Trapping near the sidelines, where the boundary acts as an extra defender.
Defensive Principles
- Stay Low: A strong defensive stance allows quick slides and reactions.
- Talk Constantly: Communication prevents breakdowns.
- Help Defense: Be ready to help a teammate if their man beats them.
- Closeouts: Sprint to shooters, then slow down with balance and hands up.
- Box Out: Secure rebounds by putting your body between the opponent and the basket.
📖 According to the NBA Coaches Association, great defense starts with discipline, communication, and teamwork.
Drills to Build Defensive Skills
Shell Drill
Teaches rotations, help defense, and communication.
Closeout Drill
Defenders sprint toward a shooter, stop under control, and contest the shot.
1-on-1 Full Court
Builds toughness by forcing players to defend their man across the entire court.
Rebounding Wars
Players compete to secure rebounds under physical pressure.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Standing upright instead of staying low
- Reaching too much instead of moving feet
- Not talking on defense
- Forgetting to box out, leading to second-chance points
Final Takeaway
Defense is the backbone of winning basketball. Whether it’s man-to-man, zone, or a full-court press, the best defenses are built on effort, communication, and trust. Strong defensive teams make opponents uncomfortable, force bad shots, and turn defense into offense.
📖 For a deeper dive into defensive footwork and fundamentals, see Breakthrough Basketball’s defensive footwork progression.